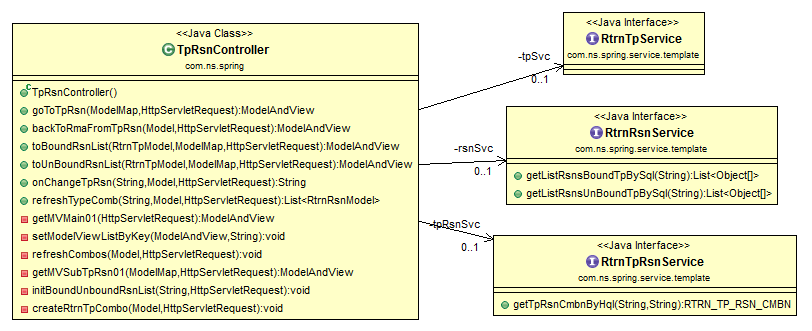
For CRUD operation in Mongo DB, you have basically two choices:
- MongoTemplate
- MongoRepository
And MongoRepository is said to be more advanced compared to MongoTemplate. MongoTemplate provide more pre-defined method than MongoRepository, but MongoRepository is very much like Generic DAO. There are some pre-defined method but you can define your custom methods.
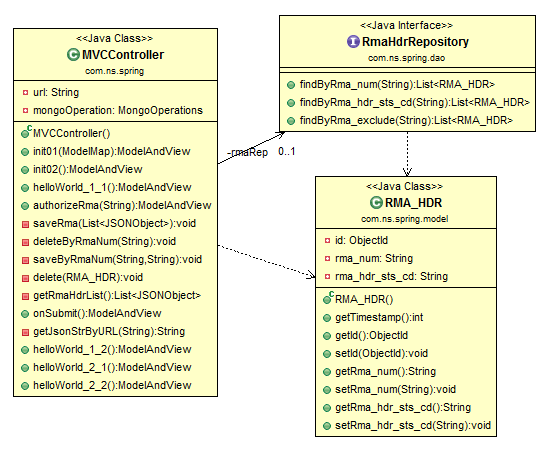
package com.ns.spring.dao;
import java.util.List;
import org.springframework.data.mongodb.repository.MongoRepository;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
import org.springframework.data.mongodb.repository.Query;
import com.ns.spring.model.RMA_HDR;
@Repository
public interface RmaHdrRepository extends MongoRepository<RMA_HDR, String>{
@Query("{rma_num : ?0}")
List<RMA_HDR> findByRma_num(String rma_num);
@Query("{rma_hdr_sts_cd : ?0}")
List<RMA_HDR> findByRma_hdr_sts_cd(String findByRma_hdr_sts_cd);
@Query("{'rma_hdr_sts_cd' : {$ne : ?0}}")
List<RMA_HDR> findByRma_exclude(String findByRma_hdr_sts_cd);
}
The syntax for MongoDB statements
In MongoDB, the table (RDB) is called “Collection”.
For inquiry: db.”collection name”.find()
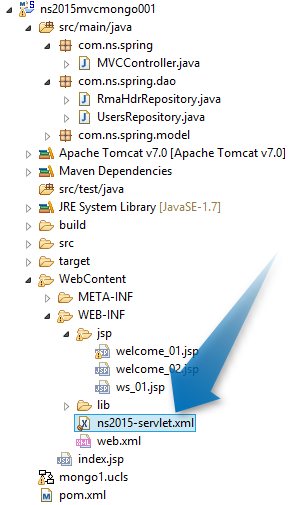
Following are some customized generic method defined in RmaHdrRepository.java (line 14 and 20). These will be executed in Mongo DB.
@Query("{rma_num : ?0}")
List<RMA_HDR> findByRma_num(String rma_num);
/* select * from rma_hdr where rma_num = 'RMA00026' */
db.rma_hdr.find({rma_num : 'RMA00026'})

@Query("{'rma_hdr_sts_cd' : {$ne : ?0}}")
List<RMA_HDR> findByRma_exclude(String findByRma_hdr_sts_cd);
/* select * from rma_hdr where rma_hdr_sts_cd <> 'auth' */
db.rma_hdr.find({'rma_hdr_sts_cd' : {$ne : 'auth'}})
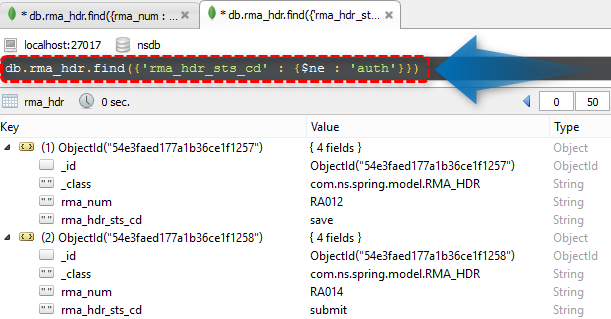
NOTE: Equivalent SQL are showing as comments.
List<RMA_HDR> list = rmaRep.findByRma_num(rma_num);
List<RMA_HDR> rmaList = rmaRep.findByRma_exclude("auth");
Called by MVCController.java at line 49, 86 and 96.
Following are non-customized method; Already provided by Mongo Repository
findAll()
save(object)
delete(object)
List<RMA_HDR> rmaList = rmaRep.findAll();
rmaRep.save(rma);
rmaRep.delete(rma);
Called by MVCController.java at line 35, 61, 81, 101, 107.
package com.ns.spring;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import org.json.simple.JSONArray;
import org.json.simple.JSONObject;
import org.json.simple.parser.JSONParser;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.ui.ModelMap;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.ModelAndView;
import com.ns.spring.dao.RmaHdrRepository;
import com.ns.spring.model.RMA_HDR;
import com.sun.jersey.api.client.Client;
import com.sun.jersey.api.client.ClientResponse;
import com.sun.jersey.api.client.WebResource;
@Controller
public class MVCController {
private String url = "http://localhost:8080/NS2015V07/ns-home/json";
@Autowired
private RmaHdrRepository rmaRep;
@RequestMapping(value = "/welcome_01")
public ModelAndView init01(ModelMap model) {
ModelAndView modelAndView = new ModelAndView("welcome_01");
List<RMA_HDR> rmaList = rmaRep.findAll();
modelAndView.addObject("rmaList", rmaList);
// mast be match with jsp name to be displayed
return modelAndView;
}
@RequestMapping(value = "/welcome_01", params = "webService", method = RequestMethod.POST)
public ModelAndView refreshByWebService() {
ModelAndView modelAndView = new ModelAndView("welcome_01");
List<JSONObject> jsonList = getRmaHdrList();
saveRma(jsonList);
List<RMA_HDR> rmaList = rmaRep.findByRma_exclude("auth");
modelAndView.addObject("rmaList", rmaList);
return modelAndView;
}
@RequestMapping("/authorize/{rmaNum}")
public ModelAndView authorizeRma(@PathVariable("rmaNum") String rmaNum) {
ModelAndView modelAndView = new ModelAndView("welcome_01");
saveByRmaNum(rmaNum, "auth");
List<RMA_HDR> rmaList = rmaRep.findAll();
modelAndView.addObject("rmaList", rmaList);
return modelAndView;
}
private void saveRma(List<JSONObject> jsonList) {
for (int i = 0; i < jsonList.size(); i++) {
JSONObject rmaJson = jsonList.get(i);
Long id = (Long) rmaJson.get("id");
String rmaNum = (String) rmaJson.get("rmaNum");
String stsCd = (String) rmaJson.get("rmaHdrStsCd");
deleteByRmaNum(rmaNum);
RMA_HDR rma = new RMA_HDR();
rma.setRma_num(rmaNum);
rma.setRma_hdr_sts_cd(stsCd);
rmaRep.save(rma);
}
}
private void deleteByRmaNum(String rma_num) {
List<RMA_HDR> list = rmaRep.findByRma_num(rma_num);
if (list != null && list.size() > 0) {
for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) {
RMA_HDR temp = list.get(i);
delete(temp);
}
}
}
private void saveByRmaNum(String rma_num, String stsNm) {
List<RMA_HDR> list = rmaRep.findByRma_num(rma_num);
if (list != null && list.size() > 0) {
for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) {
RMA_HDR temp = list.get(i);
temp.setRma_hdr_sts_cd(stsNm);
rmaRep.save(temp);
}
}
}
private void delete(RMA_HDR obj) {
rmaRep.delete(obj);
}
private List<JSONObject> getRmaHdrList() {
String output = getJsonStrByURL(this.url);
List<JSONObject> list = new ArrayList<JSONObject>();
try {
JSONParser parser = new JSONParser();
Object obj = parser.parse(output);
JSONArray array = (JSONArray) obj;
for (int i = 0; i < array.size(); i++) {
JSONObject json = (JSONObject) array.get(i);
list.add(json);
Long id = (Long) json.get("id");
String rmaNum = (String) json.get("rmaNum");
String rmaHdrStsCd = (String) json.get("rmaHdrStsCd");
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return list;
}
private String getJsonStrByURL(String url) {
Client client = Client.create();
WebResource response = client.resource("http://localhost:8080/NS2015V07/ns-home/json");
ClientResponse clientRes = response.accept("application/json").get(ClientResponse.class);
if (clientRes.getStatus() != 200) {
throw new RuntimeException("Failed : HTTP error code : " + clientRes.getStatus());
}
return clientRes.getEntity(String.class);
}
}
![]()
![]()