Working with Linux is sometime painful to encounter the issue like below. All of a sudden, you cannot login and got the error screen… If you cannot fix it, you need to re-install the system.

I have encountered this problem with my Ubuntu 14.04 (without the disappointed face icons) and this is how I got over the problem.
Step 1: Press Ctrl + Alt + f1 key to get in command mode
Step 2: Re-install the graphic drivers
Step 3: Restart the system
I have tried some methods in Step 2 but following didn’t work for my laptop probably because of its Intel Graphic driver.
Drivers for Nvidia or AMD/ATI
Nvidia:
sudo apt-get install nvidia-current
AMD/ATI:
sudo apt-get install fglrx
This method finally worked, even though, login screen looking has little changed
Intel HD Graphics:
sudo apt-get install gdm
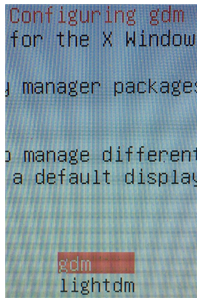
The solutions depends on the system, and this is for Intel HD Graphics.
During the install, you will be prompted to select Display Manager (DM). At this point, I choose “GDM” instead of lightDM (default for Ubuntu 14.04).
Ubuntu default login screen is lightDM, and GNOME is GDM. According to some resource, lightDM doesn’t work well in SSD. (Mine laptop is SSD). Therefore, GDM seems to be better for SSD.
sudo apt-get install numlockx sudo leafpad /etc/lightdm/lightdm.conf
In my case, the error occur after installing numlockx to enable ten-key. The command above, and adding the following line at the end of “lightdm.conf”
greeter-setup-script=/usr/bin/numlockx on
The numlockx edit lightdm.conf that change the configuration for LightDM. This is probably why I got this error.. 🙁
Updated at 2016/01/19:
This error also occur my Lubuntu with the CPU, AMD Dual-Core E1-6015, and installing gdm also fixed the problem as Ubuntu run on Intel Core i7.